
Several studies and organizations investigated deaths related to the Chernobyl accident. I present their results.
This article is part of a series on the DEC Report. The DEC report is a 200+ pages freely accessible report I wrote on climate change and energy. It assesses the world’s potential to tackle climate change by removing GHG emissions in energy and agriculture, and it assesses how we can optimize this transition.
- ➡️➡️ The DEC Report (pdf)
- 🌊 Hydropower potential (1/8)
- ☀️ Solar potential (2/8)
- 🌬️ Wind potential (3/8)
- 🏭 Nuclear potential (4/8)
- 🛢 How much fossil fuel do we consume each year? (5/8)
- 🔥 Energy, EROI and limits to growth (6/8)
- ☢️ How many people died because of the Chernobyl disaster? (7/8)
- ⚡ Why do we close nuclear reactors? (8/8)
Chernobyl
The Chernobyl disaster occurred on April 26, 1986, in Ukraine. It was caused by a combination of human error and design flaws in the reactor. The explosion and subsequent radiation release resulted in multiple deaths and the evacuation of hundreds of thousands of people.
How do we assess deaths after a nuclear disaster?
The UNSCEAR (United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation) is responsible for the assessment of radiation-related effects after a nuclear accident.
Causes of death
After a large-scale nuclear accident, several risks exist:
- There is an immediate risk for workers around the nuclear reactor, as this reactor may explode or a fire may spread.
- Secondly, there is a short-term risk of Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS) which occurs after a high dose of penetrating radiation in a very short period of time.
- Then, because of radiation risks, populations can be evacuated. These evacuations and the accident by itself can dramatically affect people’s lives, increase stress, and cause deaths.
- Finally, in the long term, in case of excessive exposure to radiations, there is a higher risk of cancer and there are risks of cancer-related deaths.
The two first causes are the easiest to measure, I’ll call them “short-term deaths”. They’re easy to measure because they usually involve a small amount of people whose health status can be monitored during a short amount of time. It may be harder to measure the two other causes because they involve much more people during multiple years. The UNSCEAR is only responsible for ionizing radiations, not for deaths related to evacuations.
Measures
When there is a large-scale nuclear disaster, a “Major accident” (7/7 INES scale), there is a major release of radioactive material with widespread health and environmental effects. UNSCEAR and other agencies assess which radioactive emissions have occurred (Xenon 133, Iode 131..), where they went, and how much radioactive material may have been released. You can see an example in this UNSCEAR report (p 192). This release can be measured in Becquerel which is a unit to measure the activity of a quantity of radioactive material.
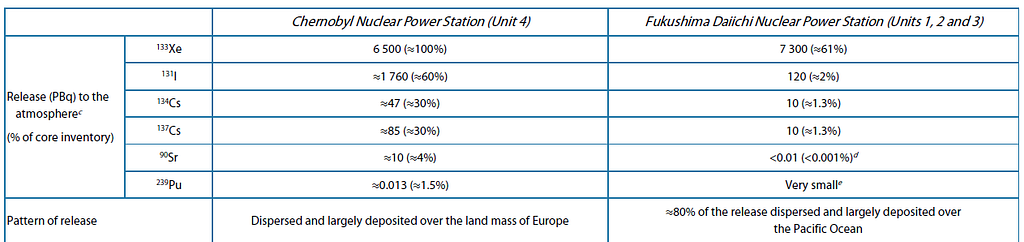
Collective exposure
Agencies now assess how much people are / have been where these emissions occured. It includes civilians and workers. And, in order to estimate how much people may be affected, it also includes animals and crops which may have been exposed and may be used to feed people.
A received dose of radioactivity is measured in Sievert. To estimate how a population was affected by radiations after an event, researchers provide a collective dose for this population. This quantity is expressed in person.Sievert (or man.Sievert). 1 man.Sievert could mean that 1 man received 1 Sievert, or that 2 men received 0.5 Sievert, or that 100 men received 10 mSv. Assuming that health consequences are statistically the same in these 3 situations is a simplification based on the Linear no-Threshold (LNT) model. Because of that, using man.Sievert to compute cancer deaths “should be avoided”.
However, even unperfect, this measure may be better than not giving any estimates. According to ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection), the “detriment adjusted nominal risk for cancer and heritable effects” is estimated at 5.5% per Sievert (table A.4.4).
According to UNSCEAR_2020_21_Report_Vol.II (p.196), the collective exposure for Chernobyl is 360000 man.sievert (200k in Belarus/Ukraine/Russia + 160k in rest of Europe).
Evacuation-related deaths
Unfortunately, there isn’t one official number for evacuation-related deaths for Chernobyl. The analysis has been performed on Fukushima but not for Chernobyl. Officially, 340000 people have been evacuated or relocated post-Chernobyl (UNSCEAR report, p.192).
Review of numbers in multiple studies
I included 6 studies or reports from organizations in this review: UNSCEAR 2000V2J, WHO, UNSCEAR 2008V2D, OWID, Sovacool, Hirschberg1998.
Short-term deaths
There is broad consensus on the 31 deaths that occurred shortly after the explosion or due to the acute radiation syndrome.
Long-term radiation-related deaths
- WHO: 4000
- UNSCEAR 2008V2D: 9000
- OWID: 385
- Sovacool (all deaths): 4056
- Hirschberg1998: 32700
These measures are done with a DDREF (Dose and Dose Rate Effectiveness Factor) of 2. Basically the DDREF estimates in a simplified way how dangerous low-level radiation exposure is. With a DDREF of 1, deaths would be higher. In literature, a value of DDREF between 1 and 2 can be found. But, in literature, there is also no consensus on the dangers of low-level exposure to ionizing radiation.
Evacuation-related deaths
There is no official estimate of the number of evacuation-related deaths at Chernobyl. For Fukushima, it is estimated that 2326 people may have died because evacuation-related deaths. This is 2.6% of evacuees. For Chernobyl, if 2.6% of evacuees died because of the evacuation, there would be 8986 evacuation-related deaths.
Results
If we take the highest numbers for short-term related deaths, long-term radiation-related deaths, and evacuation-related deaths, we can estimate that 31+32700+8986 = 41717 people at most died because of Chernobyl. Lower and higher numbers could be provided. Lower numbers could be provided because I took the highest estimate for long-term radiation-related deaths. Higher numbers could be provided because of the DDREF = 2 hypothesis and because all deaths related to the accident need to be considered: evacuation, stress, economic difficulties, worst living conditions etc.
Links
You can see how some of these results were used in much more details in the DEC report. Some of the data and models I used are also available on Github.
👏 if you liked this article and I’ll do more!